anterior labral tear shoulder test|how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff : warehouse Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and . Resultado da Privacy and Security Help Page. This page links to our help articles that answer privacy and security questions. We try to make information easy .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBOur platform is most compatible with: Google Chrome Safari. Responsible Gaming Policy 21+ Responsible Gaming. Date / Name
speed's test vs o'brien's
The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) . See moreYour shoulder is a large and complex joint. The O’Brien test focuses on your AC joint and labrum. Your AC joint is one of four shoulder joints, where two bones . See moreHealthcare providers who may perform the O’Brien test include: 1. Athletic trainers. 2. Orthopedists(bone and joint specialists). 3. Physical therapists. 4. . See more
The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] .
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and .
Diagnosing Labral Tears of the Shoulder. To evaluate for a possible shoulder labrum tear, a Penn orthopaedic specialist will examine your shoulder, conduct several physical tests to check your range of motion, take a full health history .Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an MRI, CT scan and/or arthroscopy of the shoulder. Treatment varies depending on type, severity and location of the labrum tear.O’Brien’s Test is a special orthopaedic/orthopedic test for the shoulder that attempts to test specifically for glenohumeral joint labral tears (and more specifically for SLAP Lesions; .
The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or .
Superior Labrum, Anterior to Posterior tears (SLAP tears), also known as labrum tears, happen when you tear cartilage in the inner part of your shoulder joint.Imaging Tests. Your doctor may order an MRI scan to determine whether you have a shoulder labral tear or another type of injury causing your symptoms, such as a fracture or torn rotator .
For example, orthopaedic surgeons can now use miniaturized instruments and cameras (arthroscopic surgery) to see inside a joint. This enables them to identify and treat a shoulder injury called a glenoid labrum tear, also known as a labral . A posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex, and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. Diagnosis can be made clinically with . Superior Labrum, Anterior to Posterior tears (SLAP tears), also known as labrum tears, happen when you tear cartilage in the inner part of your shoulder joint. . Shoulder Labral Tear Treatment. Find a Doctor and Specialists. Make an Appointment. Contents. . Providers use the following tests to diagnose SLAP tears and determine treatment .Positive Test [edit | edit source]. Clunk or Grinding: A clunking or grinding sensation is felt or heard, indicating a possible labral tear. Pain: The presence of pain during the maneuver can also indicate a positive test. Significance [edit | edit source]. Labral Tear: The test is particularly useful for identifying superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions.
Posterior Labral Tear Neurovascular Disorders . performed by flexing shoulder to 90°, flex elbow to 90°, and forcibly internally rotate driving the greater tuberosity farther under the CA ligament. . NOTE: positive anterior release is really a "3 in 1" test - if it is positive, apprehension and relocation are also positive. Anterior . Am Fam Physician. 2000;61(10):3079-3088 This is Part I of a two-part article on clinical evaluation of the painful shoulder. Part II, “Acute and Chronic Injuries,” will appear in the next .

special tests for shoulder labrum
Before proceeding with the examination of the shoulder it is very important to complete a full examination of the cervical spine to make sure that no spinal pathologies are contributing to the presentation. . Any asymmetries in the rhytm of scapular movement would indicate pathology in the anterior aspect of the shoulder. Observe for scapular .The labrum: A fibrous ring of cartilage which extends up from the glenoid providing stability in the form of a deeper cup for the humeral head to fit into. . An evaluation of the apprehension, relocation, and surprise tests for anterior shoulder instability. The American Journal of Sports Medicine 2004;32(2):301-7. Ongoing shoulder pain or other symptoms should prompt a visit to your doctor. After a physical exam, your doctor will likely order some tests. There is no specific shoulder labrum tear test, such as by moving your shoulder a certain way. Instead, doctors rely on imaging exams and sometimes, arthroscopy, to diagnose the problem. X-rays can show . Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Instability (TUBS) . A SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and biceps tendonitis. . "peel back" test shows "peel back" of the labrum .
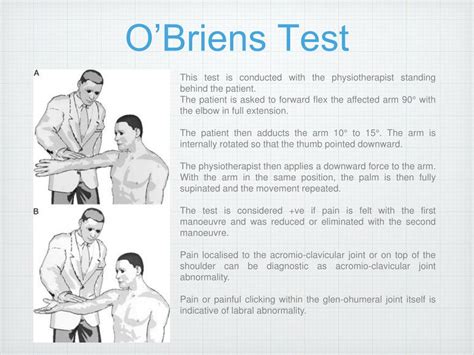
Explanation of O'Brien's Test in orthopedic shoulder examination including involved tissues, test postion, test movement, etc. plus video demonstration. Skip to content. . superior labral tear from anterior to posterior). A false positive may occur if there is an injury to the rotator cuff or acromioclavicular (AC) joint. Involved Structures .
An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Labral tears cause groin pain or pain in the anterior side of the hip, and less commonly buttock pain. This mechanically induced pathology is thought to result from excessive forces at the hip joint. For example, a tear could decrease the acetabular contact area . Shoulder dislocations are the most common type of shoulder injuries. They affect about 1% of the population. About 90% of shoulder dislocations are anterior, which means to the front of the socket. Anterior shoulder dislocations are most likely to cause a glenoid labrum tear — and between 87% and 100% of them do. This type of shoulder labral tear occurs at the top (“superior”) of the glenoid labrum where it connects to the biceps tendon, and it extends in a curve from the chest (“anterior”) to the back (“posterior”). SLAP lesions are considered as separate entities from other labral tears because the superior labrum is the attachment site of . A SLAP tear of the shoulder is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder joint. SLAP tears typically cause pain when performing overhead activities. . SLAP stands for superior labrum from anterior to posterior. . These tests are part of a shoulder examination. The most common tests include O'Brien's test (active compression test) and crank test:
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous complex that attaches as a rim to the articular cartilage of the glenoid fossa. Its role is to deepen and increase the surface area of the glenoid (acting as a static stabiliser of the glenohumeral joint); resist anterior and posterior movement and assist with blocking shoulder dislocation and subluxation at the maximal ranges of motion.
Anterior Drawer Test of the shoulder is used to examine the Anterior shoulder instability. It can also be used on aching shoulders where the apprehension test is difficult to interpret, and it has allowed us to reliably diagnose anterior subluxations even in patients who may have a negative apprehension test. [1]A shoulder labral tear is an injury to the ring of cartilage in the shoulder joint. Two of the most common tears are the SLAP (Superior Labral tear form Anterior to Posterior) tear and the Bankart tear. . Take a complete health history and conduct a physical examination to assess your tear, pinpoint the location, and check your range of . Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Instability, . Diagnosis is made clinically with the presence of positive anterior instability provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies that may reveal labral and/or bony injuries of the glenoid and proximal humerus (Hill-Sachs lesion). . is an avulsion of the anterior labrum and anterior band of the IGHL .
Diagnosing a posterior labral tear of the shoulder can be difficult for physicians. These tears can present with a wide variety of symptoms and there are multiple physical exam tests of undetermined significance. Posterior shoulder instability is less commonly seen than anterior instability and the incidence is 2-5% (3).
The glenoid labrum is integral to shoulder stability and can be difficult to assess clinically. Whilst it is a single anatomical structure, damage to different regions results in very different clinical manifestations. . An evaluation of the apprehension, relocation, and surprise tests for anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med 2004 .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Apprehension test is generally used to test the integrity of the glenohumeral joint capsule, or to assess glenohumeral instability in an anterior direction.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patient should be position in supine. The therapist will flex the patient's elbow to 90 degrees and abducts the patient's shoulder to 90 degrees in sagittal . Anterior dislocations of the shoulder can be associated with a disruption of the anteroinferior labrum and anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament, also known as a Bankart lesion. . Pain provocative test : Patient abducts shoulder to 90 degrees, flexes elbow to 90 degrees, and pronates and supinates the hand : A torn labrum in the shoulder commonly occurs due to overuse or injury. Learn more about the types of tear and their symptoms and treatment options here.
Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of .
webLojas Kalunga. Tem sempre uma loja pertinho de você! Nossas lojas não possuem serviços de atendimento telefônico. Para contato, dirija-se a um de nossos 225 Endereços.
anterior labral tear shoulder test|how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff